Ray tracing requires the solution of the ray equations to determine the ray coordinates.
Amplitude and acoustic pressure requires the solution of the dynamic ray equations,
which are described in detail in [1].
For a system with cylindrical symmetry the ray equations can be written as [2]
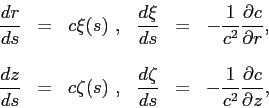 |
(1) |
where 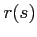 and
and 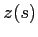 represent the ray coordinates in cylindrical coordinates
and
represent the ray coordinates in cylindrical coordinates
and 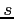 is the arclenght along the ray;
the pair
is the arclenght along the ray;
the pair
![$c(s)\left[ \xi(s),\zeta(s) \right] $](img7.png) represents the tangent versor along the ray.
Initial conditions for
represents the tangent versor along the ray.
Initial conditions for 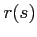 ,
, 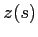 ,
, 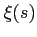 and
and 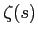 are
are
where 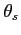 represents the launching angle,
represents the launching angle,
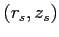 is the source position,
and
is the source position,
and 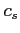 is the sound speed at the source position.
The coordinates are sufficient to obtain the ray travel time:
is the sound speed at the source position.
The coordinates are sufficient to obtain the ray travel time:
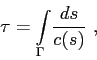 |
(2) |
which is calculated along the curve
![$\left[ r(s),z(s) \right] $](img15.png) .
.
Orlando Camargo Rodríguez
2008-06-16