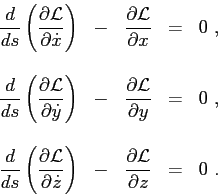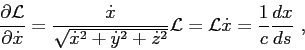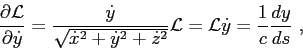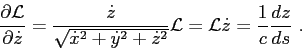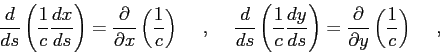Based on Lagrangian's formalism one can write Eq.(2.9) as
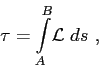 |
(2.10) |
where 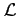 represents the system's Lagrangian:
represents the system's Lagrangian:
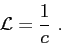 |
(2.11) |
Within the context of the formalism 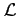 is supposed to be a function of
coordinates and generalized velocities[5]:
is supposed to be a function of
coordinates and generalized velocities[5]:
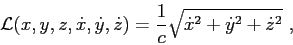 |
(2.12) |
where
In this way,
the perturbation of the travel time corresponds to
According to Fermat's principle
which implies that
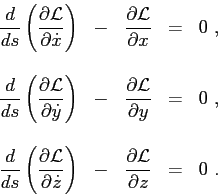 |
(2.13) |
On the other side, using Eq.(2.12) one can obtain that
Therefore,
one can conclude that the solution of the Eikonal equation requires the solution of the following system of equations:
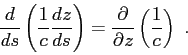 |
(2.14) |
Orlando Camargo Rodríguez
2012-06-21
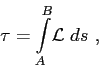
![\begin{displaymath}
\delta \tau = \displaystyle{ \int\limits_{A}^{B}} \left\{
\...
...L}}}{\partial{\dot{z}}}\delta \dot{z} \right]
\right\} ds =
\end{displaymath}](img36.png)
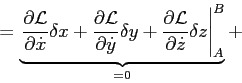
![\begin{displaymath}+
\displaystyle{ \int\limits_{A}^{B}}
\left\{
\left[ \fra...
...partial{\dot{z}}} \right) \right] \delta z
\right\} ds .
\end{displaymath}](img38.png)