|
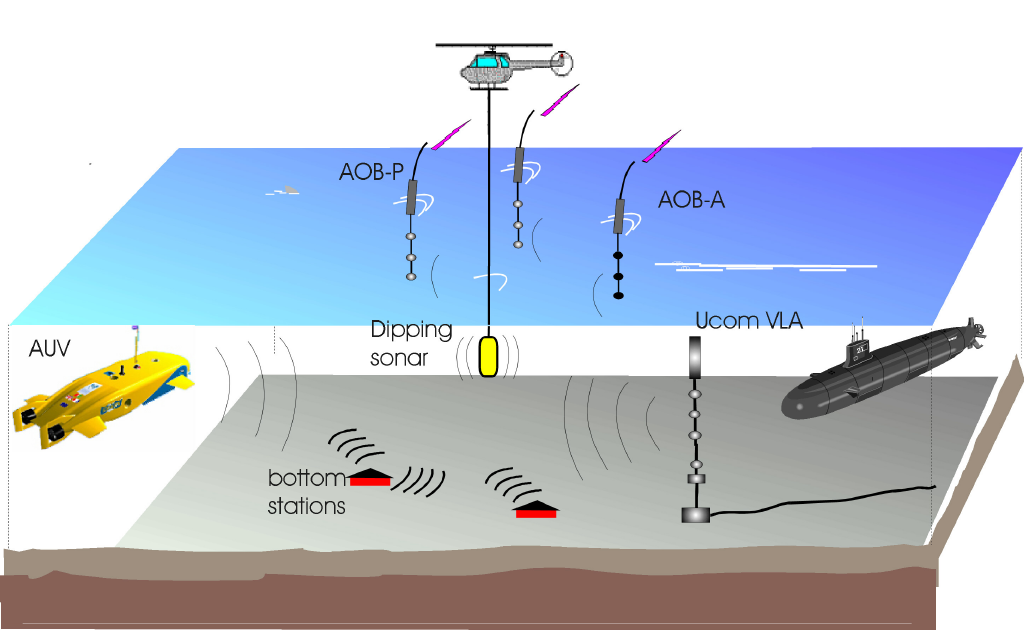
Image: AOB system composed of three AOBs, two passive
(listening only) and one active (listening and emitting). AOBs
are free drifting GPS located, self recording and at all time monitored
via a wireless lan network. Represented applications include: global
underwater positioning/tracking of cooperating platforms (such as
AUVs), coherent underwater communications with subs, AUVs, bottom
stations or shore linked hubs, rapid environmental assessment via full
field inversion of both water column and bottom properties for
prediction systems initialization and active/passive source detection,
classification and localization.
|




