Boundary reflections
The decaying factor 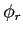 is given by the expression
is given by the expression
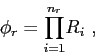 |
(4.1) |
where 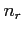 represents the total number of boundary reflections,
and
represents the total number of boundary reflections,
and 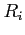 is the reflection coefficient at the
is the reflection coefficient at the 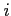 th reflection.
The case with no reflections (
th reflection.
The case with no reflections (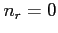 ) corresponds to
) corresponds to 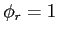 .
Generally speaking, boundaries can be one of four types:
.
Generally speaking, boundaries can be one of four types:
- Absorvent: the wave energy is transmitted completely to the medium above the boundary,
so
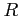 = 0 and ray propagation is terminated at the boundary.
= 0 and ray propagation is terminated at the boundary.
- Rigid: the wave energy is reflected completely on the boundary,
with no phase change, so
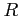 = 1.
= 1.
- Vacuum: the wave energy is reflected completely on the boundary,
with a phase change of
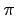 radians, so
radians, so 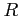 = -1.
= -1.
- Elastic: the wave energy is partially reflected, with
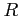 being a complex value and
being a complex value and
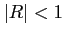 .
.
The calculation of the reflection coefficient for an elastic medium (see Fig.4.1)
is given by the following expression[10]:
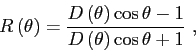 |
(4.2) |
where
where the units of attenuation should be given in dB/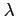 .
.
Figure 4.1:
Ray reflection on an elastic media.
|
|
In general the reflection coefficient is real when
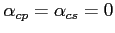 ,
and the angle of incidence
,
and the angle of incidence 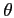 is less than the critical angle
is less than the critical angle 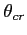 ,
with
,
with 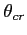 given by the expression
given by the expression
 |
(4.3) |
Moreover,
attenuation is negligible when
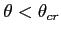 ,
and for small
,
and for small 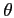 the energy transfered to shear waves in the elastic medium is only a small fraction
of the total energy transfered.
the energy transfered to shear waves in the elastic medium is only a small fraction
of the total energy transfered.
Orlando Camargo Rodríguez
2012-06-21
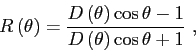
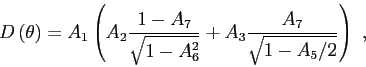
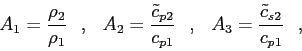
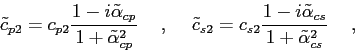
![]() ,
and the angle of incidence
,
and the angle of incidence ![]() is less than the critical angle
is less than the critical angle ![]() ,
with
,
with ![]() given by the expression
given by the expression