Volume attenuation in the ocean has a chemical nature,
and it is induced by relaxation processes of salt constituents like MgSO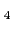 , B(OH)
, B(OH)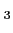 and MgCO
and MgCO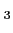 .
.
The factor 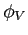 is given by the decaying exponential
is given by the decaying exponential
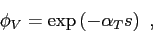 |
(4.4) |
where 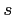 is the ray arclength and
is the ray arclength and
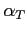 is the Thorpe (frequency dependent) attenuation coefficient in dB/m,
given by[2]
is the Thorpe (frequency dependent) attenuation coefficient in dB/m,
given by[2]
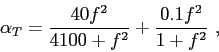 |
(4.5) |
with the frequency given in kHz.
Orlando Camargo Rodríguez
2012-06-21
![]() is given by the decaying exponential
is given by the decaying exponential